Understanding U.S. Electrical Standards: A Guide for Designers, Engineers, and Contractors
Understanding U.S. Electrical Standards: A Guide for Designers, Engineers, and Contractors
When designing electrical systems or undertaking electrical installations in the United States, it’s essential to understand and comply with the country’s electrical standards. These standards ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Whether you’re an electrical designer, contractor, or engineer, having a clear grasp of these regulations is crucial for a successful project.
What Are U.S. Electrical Standards?
U.S. electrical standards are a set of codes and regulations that dictate how electrical systems should be designed, installed, and maintained. They aim to ensure safety for individuals and property, promote energy efficiency, and standardize practices across the industry. These standards are primarily outlined in documents that are periodically updated by various organizations, including the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), and the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA).
The primary standard governing electrical systems in the U.S. is the National Electrical Code (NEC), which is published by the NFPA.
1. National Electrical Code (NEC)
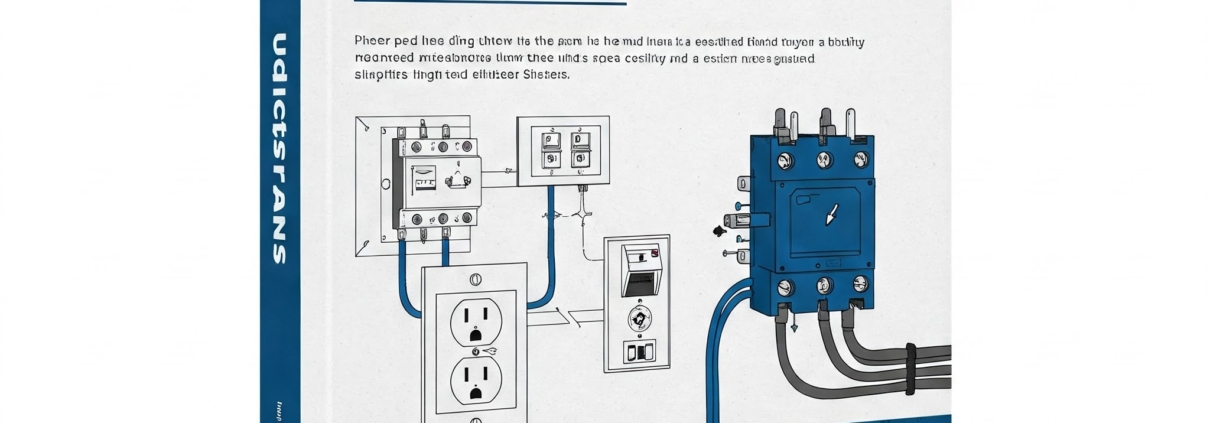
The NEC is the most important standard for electrical installations in the U.S. It is updated every three years and is adopted by states and municipalities to ensure safe electrical practices across the country. The code outlines the minimum requirements for the installation of electrical wiring, equipment, and devices in buildings and structures.
Key Areas Covered by the NEC:
- Wiring and Protection: Specifications on proper wiring materials, installation techniques, and protection against overloads or short circuits.
- Grounding and Bonding: Guidelines on grounding electrical systems to prevent shock hazards and ensure safety during faults.
- Circuit Requirements: Regulations for the number and type of circuits required for various types of loads (e.g., lighting, appliances, HVAC systems).
- Lighting and Receptacles: Proper placement, installation, and maintenance of electrical lighting and receptacle outlets.
- Electrical Equipment: Standards for electrical panels, transformers, motors, and other equipment.
The NEC does not dictate design methods but sets the baseline safety requirements that must be adhered to. It’s important to check the local adoption of the NEC, as some regions may have additional amendments or specific interpretations of the code.
2. The National Electrical Safety Code (NESC)
The NESC is another key standard that applies primarily to electrical utility systems rather than residential or commercial electrical systems. Published by the IEEE, the NESC focuses on safety practices for overhead and underground electric power distribution and transmission systems.
It includes requirements for:
- Power Lines: Safe clearance distances, construction standards, and maintenance practices for power lines.
- Electrical Worker Safety: Best practices to protect electrical workers from electrical hazards, especially in high-voltage environments.
- Equipment Standards: Guidelines for substations, transformers, and other utility equipment.
3. ANSI Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) is responsible for coordinating the development of national consensus standards. ANSI standards address various aspects of electrical equipment and components used in construction and industrial operations. These standards ensure compatibility and interoperability of electrical products across different manufacturers.
Some key ANSI standards include:
- ANSI C84.1: Voltage Ratings for Electrical Systems
- ANSI C12: Standards for Electric Meters
- ANSI/IEEE C37: Switchgear and Circuit Breaker Standards
4. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Standards
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an independent organization that tests and certifies electrical products for safety. UL standards cover a wide range of electrical equipment and devices, including lighting fixtures, electrical panels, and consumer electronics.
When installing electrical products, it’s crucial to ensure they are UL-listed, meaning they meet the necessary safety standards and have been tested for fire, shock, and environmental hazards.
5. State and Local Codes
In addition to the NEC, each state or municipality in the U.S. may have its own amendments or additional codes specific to local conditions. For instance, California has its own set of electrical regulations known as the California Electrical Code (CEC), which is based on the NEC but includes state-specific rules regarding energy efficiency and earthquake-resistant design.
Before starting a project, it’s important to verify the local codes that apply to ensure full compliance. Local inspectors and regulatory authorities often conduct thorough reviews to ensure all electrical installations adhere to the relevant codes.
6. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Standards
With growing concerns about energy conservation and environmental sustainability, energy efficiency has become an integral part of U.S. electrical standards. These standards are often incorporated into national, state, and local codes.
Title 24 of the California Code of Regulations, for example, includes stringent energy efficiency requirements for lighting and electrical systems. These standards aim to reduce energy consumption in commercial and residential buildings.
Additionally, the Energy Policy Act (EPACT) and Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) standards provide guidelines for sustainable building practices, including energy-efficient electrical designs and green building certifications.
Why Are These Standards Important?
- Safety: The primary purpose of these standards is to protect lives and property by preventing electrical hazards such as shocks, fires, and electrocution.
- Consistency: U.S. electrical standards ensure uniformity in electrical design, installation, and maintenance practices, making it easier for professionals to work across regions.
- Compliance: Adhering to the codes and standards ensures compliance with the law and can protect professionals from liability issues. It’s also crucial for passing inspections.
- Energy Efficiency: With energy costs on the rise and sustainability becoming a major concern, these standards promote more efficient use of electricity, which can result in long-term savings for both users and businesses.
- Future-Proofing: Standards such as the NEC and NESC evolve with advancements in technology, ensuring that electrical systems are ready for emerging technologies like smart grids, renewable energy integration, and electric vehicles.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!